Creating SSH Keys for use with DMC
Overview
This guide walks you through creating SSH key pairs for DMC to scan physical Linux servers. DMC requires SSH keys to establish secure connections and collect configuration and performance data from Linux servers without requiring password authentication.
SSH Key Requirements
Before creating your SSH keys, ensure they meet DMC’s requirements:
| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| Supported Algorithms | RSA, DSA, ECDSA, ed25519 |
| Format | OpenSSH format only |
| Passphrase | No passphrase (not supported) |
| Compatibility | PuTTY-generated keys not supported |
Creating SSH Keys
Using ssh-keygen (Recommended)
The ssh-keygen command is the standard tool for creating SSH key pairs on Linux, macOS, and Windows (with OpenSSH).
Basic Key Generation
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -f ~/.ssh/dmc_key -N ""Parameters explained:
-t rsa: Specifies RSA algorithm (you can also usedsa,ecdsa, ored25519)-b 4096: Sets key size to 4096 bits for RSA (recommended for security)-f ~/.ssh/dmc_key: Specifies the output filename-N "": Sets empty passphrase (required for DMC)
Alternative Key Types
For ECDSA (recommended for modern systems):
ssh-keygen -t ecdsa -b 521 -f ~/.ssh/dmc_key -N ""For ed25519 (most modern and secure):
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -f ~/.ssh/dmc_key -N ""For DSA (legacy support):
ssh-keygen -t dsa -b 1024 -f ~/.ssh/dmc_key -N ""Key File Management
File Permissions
After creating your SSH keys, set proper permissions:
Linux/macOS:
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/dmc_key
chmod 644 ~/.ssh/dmc_key.pubWindows (PowerShell):
icacls "C:\Users\$env:USERNAME\.ssh\dmc_key" /inheritance:r /grant:r "$env:USERNAME:(R)"
icacls "C:\Users\$env:USERNAME\.ssh\dmc_key.pub" /inheritance:r /grant:r "$env:USERNAME:(R)"Key Storage
Store your SSH keys in the standard location:
| Platform | Private Key Path | Public Key Path |
|---|---|---|
| Linux/macOS | ~/.ssh/dmc_key |
~/.ssh/dmc_key.pub |
Deploying Public Keys
Copy Public Key to Target Servers
You need to copy the public key to each Linux server you want DMC to scan.
Method 1: Using ssh-copy-id (Linux/macOS)
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/dmc_key.pub username@target-serverMethod 2: Manual Copy
cat ~/.ssh/dmc_key.pub | ssh username@target-server "mkdir -p ~/.ssh && cat >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys"Method 3: Direct File Copy
scp ~/.ssh/dmc_key.pub username@target-server:~/.ssh/
ssh username@target-server "cat ~/.ssh/dmc_key >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys"Set Proper Permissions on Target Servers
After copying the public key, ensure proper permissions on the target server:
chmod 700 ~/.ssh
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keysTesting SSH Key Authentication
Verify Key-Based Authentication
Test that your SSH key works before using it with DMC:
ssh -i ~/.ssh/dmc_key username@target-serverIf successful, you should connect without being prompted for a password.
Troubleshooting Authentication Issues
If authentication fails, check:
- Key permissions on both local and remote systems
- SSH configuration on the target server
- Key format (ensure it’s OpenSSH format)
- Server SSH settings (ensure public key authentication is enabled)
DMC Configuration
Adding SSH Keys to DMC
Once your SSH keys are created and deployed:
- Upload the private key to DMC through the web interface
- Configure the username for each target server
- Test connectivity using DMC’s validation tools
Key Rotation
For security best practices:
- Rotate SSH keys periodically (every 90-180 days)
- Remove old keys from target servers when rotating
- Update DMC configuration with new keys
Security Considerations
Key Protection
- Keep private keys secure and never share them
- Use strong key sizes (4096 bits for RSA, 521 for ECDSA)
- Limit key access to only necessary systems
- Monitor key usage for unauthorized access
Server Hardening
- Disable password authentication after confirming key-based auth works
- Use fail2ban or similar tools to prevent brute force attacks
- Regular security updates for SSH services
- Audit SSH access logs regularly
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Using a PuTTY-generated SSH key
As detailed in the SSH key requirements, PuTTY-generated keys not supported.
SSH keys will need to be converted to a passphraseless OpenSSH formatted key.
This can be done within PuTTYgen:
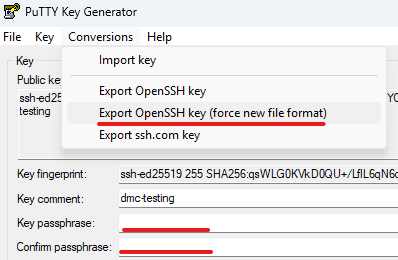
Converting a Putty generated SSH key
“Permission Denied” Errors
Check file permissions:
ls -la ~/.ssh/Verify key ownership:
chown username:username ~/.ssh/dmc_key“No Such File or Directory” Errors
Ensure SSH directory exists:
mkdir -p ~/.ssh
chmod 700 ~/.ssh“Bad Permissions” Errors
Fix key file permissions:
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/dmc_key
chmod 644 ~/.ssh/dmc_key.pubSummary
Creating SSH keys for DMC involves:
- Generating key pairs using
ssh-keygenwith no passphrase - Setting proper permissions on both local and remote systems
- Deploying public keys to target Linux servers
- Testing authentication before DMC configuration
- Configuring DMC with the private key and usernames
Following these steps ensures secure, passwordless authentication for DMC to scan your Linux servers and collect the necessary data for migration assessment.